RTI: Response to Intervention
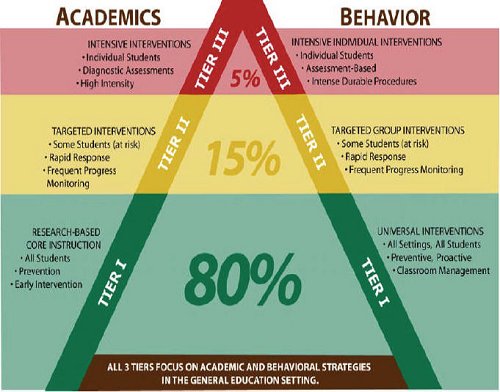 District 53 implemented a Response to Intervention model in 2009. New Federal laws (NCLB 2001 and IDEA, 2004) comprise the driving force behind this implementation model. Response to Intervention (RtI) is a flexible approach to providing appropriate academic and behavioral supports as determined by students’ individual needs. RtI allows schools to intervene early for struggling learners by supporting them within a multi-tier model rather than waiting for them to fail.
District 53 implemented a Response to Intervention model in 2009. New Federal laws (NCLB 2001 and IDEA, 2004) comprise the driving force behind this implementation model. Response to Intervention (RtI) is a flexible approach to providing appropriate academic and behavioral supports as determined by students’ individual needs. RtI allows schools to intervene early for struggling learners by supporting them within a multi-tier model rather than waiting for them to fail.
RtI encompasses a variety of procedures used to determine how specific changes in instruction affect student achievement. RtI allows problem-solving teams within the school to design, implement, and evaluate educational interventions.
Benefits of the RtI approach include helping students receive prompt, appropriate support within the general education setting. The number of students who are successful within regular education will increase as tiered supports are provided. Students will be less likely to be identified as having a disability when achievement problems may be due to other issues. The State of Illinois required that all school districts submit an RtI Plan by January of 2009.
RtI provides schools with an alternative to traditional identification procedures for Special Education. However, RtI is NOT Special Education. RtI provides services for ALL students within the three-tier model.
If a student does not respond to the intensive, high-quality instruction that is part of the Tier 3 RtI services, the school's problem-solving team (SST) may examine student performance history to uncover further causes of the student's specific learning problems. The student's performance within the RtI model will be evaluated by the team. These assessments will be used along with other information to determine the next course of action.
RTI Terms
Response to Intervention (RtI): A model that integrates assessment and intervention within a multi-level prevention system to maximize student achievement.
Universal Screening: An assessment given to all students, typically threetimes a year, to determine each student's level of proficency in essential academic areas and behaviors i.e., Math, Writing, or Reading Curriculum-Based Measures, a Guided Reading Benchmark Assessment.
Intervention: A change in instruction for a student in an area of learning or behavior difficulty in order to improve performance and achieve adequate progress.
Progress Monitoring: Scientifically-based practice utilized to frequently assess student performance and evaluate the effectiveness of instruction and/or interventions.
Research-based Instruction: Specific strategies proven to beeffective. The research has been reported in scientific, peer-reviewed journals.
